Last updated on May 6th, 2023 at 12:35 pm
Our bodies are constantly going through changes throughout our lives. From the time we are conceived in our mother’s womb until we die, our cells constantly die and get replaced. According to some estimates we have at least 30-50 trillion bacteria in our bodies, which is almost double the amount of human cells. The large population of bacteria and microorganisms living inside and on our bodies indicates their crucial importance for our body’s long-term survival.
These bacteria and other microorganisms play a vital role in our health and wellness. Our microbiome adapts itself to our environment and, in the long run, affects our immune response and how our bodies react to pathogens, diseases, and infections. These bacteria also aid in digestion by breaking down certain components of food that we cannot digest naturally such as inulin. The human microbiome differs from person to person due to factors like culture, location, and environment. A sudden change in the microbiome can lead to several problems and many chronic health issues in the long run.
While we are often taught to prioritize cleanliness and use antibacterial products regularly, this modern habit may create a misconception that all kinds of bacteria are harmful.
In reality, the constant use of sanitizers and antibacterial soaps not only kills harmful bacteria but also kills off the beneficial bacteria, viruses, and fungi that our bodies need to stay healthy. These “good bacteria” are referred to as probiotics, along with certain viruses and fungi, such as yeast.
What are Probiotics?
Probiotics are defined as microorganisms that have positive health effects on the user when consumed in an adequate amount. In modern research, fermented food has been found to carry a host of ‘good’ bacteria or fungi which is supposed to be a major reason for many benefits of fermented food.
Humans have a long history of consuming fermented food including kimchi, kefir, kombucha, yogurt, and sour milk. Historically, the benefits of fermentation were not only talked about by the Romans but it has been a part of religious myths also, associated with long life and a strong body.
In 1905, Bulgarian microbiologist Stamen Grigorov identified the first strain of probiotics known as Lactobacillus bulgaricus. Since then several probiotic strains have been identified and used for their many benefits.
Probiotics work by promoting homeostasis in the body and repopulating the microbiome with beneficial microorganisms. In the gut, probiotics help with the process of food digestion and compete for resources against harmful bacteria. When our body is fighting off an infection probiotics help us by releasing certain enzymes like fencing which kill off even antibiotics-resistant infectious microorganisms. Probiotics also produce vitamins, help in the breakdown of certain medications, and strengthen the cell line of the gut to prevent harmful bacteria from entering our blood.
We carry Most of our probiotics in the gut and in organs like the mouth, urinary tract, lungs, and skin. Although Probiotics are present all over our bodies, organs that are exposed to external environments make for a good place for probiotics to thrive.
Some of the most common types of probiotic strains belong to either Lactobacillus or Bifidobacterium groups.
Lactobacillus is found in dairy products and breaks down milk protein, bifidobacterium is found in the intestines and fights off harmful bacteria. Both of these groups of probiotics are used to prevent several health issues.
Other than lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, probiotics like bacteriophage or Saccharomyces Boulardii are nonbacterial sources of probiotics.
Probiotics Benefits
Probiotics are one of the most used supplements around the world. According to the US Health interview survey, more than 3.9 million adults in the USA have used either probiotics or prebiotics. In 5 years(2007-12) users of probiotics supplements increased four times. This popularity is certainly not only because of the digestive benefits of probiotics which is the primary reason many of us use probiotics but there are several other benefits including:
Immunity Response
Probiotics regulate the gut microbiome which affects our immune response. Probiotics help in increasing the production of antibodies against viral infections such as rhinovirus flu and accelerate recovery.
Probiotics like BL-04® have been tested for immune response in several studies which proves their effectiveness in aiding the body’s immune system.
In a study done on subjects suffering from inflammatory bowel disease a combination of probiotics reduced and reversed the effects of e.coli-induced inflammation in the bowel. Probiotics decrease proinflammatory signaling molecules such as cytokines and chemokines which cause inflammation in the body.
These immunity regulating and antiinflammatory properties of probiotics are being studied and as we get more data our understanding would evolve on how to better use probiotics for immune response.
Insulin Sensitivity
Probiotics increase the metabolic rate of your body, help in digestion and reduce inflammation which is one of the major reasons for insulin resistance. Inflammation triggers the production of cytokines, these molecules if left unchecked cause insulin resistance in the cells. Probiotics like Bacillus Coagulans show immune-modulating effects and can control the production of cytokines.
Additionally, probiotics produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) like acetate, butyrate, and propionate and they also regulate hormones like Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Both SCFAs and GLP-1 increase insulin secretion and sensitivity.
Mental Health
Several research studies indicate that the gut microbiome can affect mood, psychological health, and brain function. This is because of the gut-brain axis which is a complex system of communication between our brain and the gut. This axis is affected by several factors and probiotics are one of those factors.
In one study published in the journal Brain, Behavior, and Immunity researchers observed that individuals who took probiotics showed a lower affinity to psychological distresses like anxiety, stress, and depression.
Some preliminary research suggests that probiotics can lower the severity of autism and other cognitive impairments including PTSD and OCD. However, we don’t fully understand how probiotics affect our brains and more research is needed to have a conclusive opinion on some of the emerging psychological health benefits of probiotics.
Cardiovascular Health
Probiotics have cardioprotective properties as they are known to lower inflammation, increase lipid metabolism, and clear plaque buildup from the arteries all of which lower the risk of heart attack, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases (CVD).
A meta-analysis of 9 trials indicates that probiotics caused a significant reduction in the systolic and diastolic blood pressure in the participants.
Allergy and Skin Health
Allergies can be caused as a result of our immune response to natural substances like pollen, nuts, and dust. As many probiotics have anti-inflammatory and immunity-modulating properties they can prevent allergic reactions by preventing inflammation.
A review of more than 20 studies and clinical trials shows that probiotics reduce the chances of allergic reactions such as eczema and rhinitis in both adults and children.
Probiotic strains like Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, and Lactobacillus acidophilus can be used to prevent skin conditions like eczema and acne.
The effect of probiotics on the skin is probably because of some connection between the gut microbiome and the skin microbiome which is part of one single microbiome. However, the exact mechanism of how gut probiotics affect the skin is yet to be established.
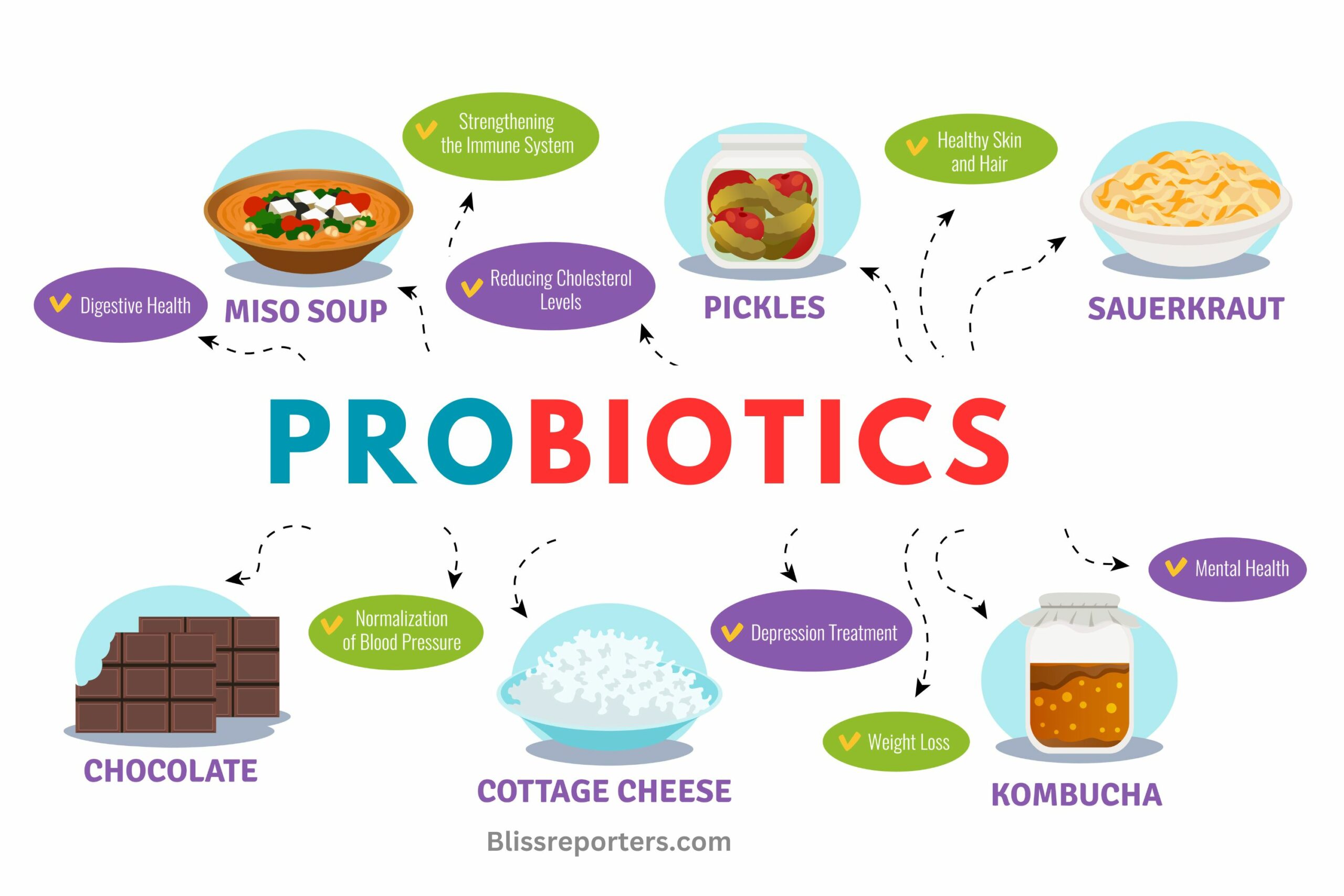
Food Sources of Probiotics
The best way to get probiotics at home is to ferment your own food. Fermentation not only keeps your foods and vegetables edible for much longer, but it also makes them a potent probiotic supplement.
However, if you are low on time there are foods that are naturally rich in probiotics, such as:
- Yogurt
- Kefir
- Sauerkraut
- Tempeh
- Kimchi
- Miso
- Kombucha
- Buttermilk
- Natto
- Skyr
- Turshi
- Pickled vegetables
- Unprocessed Cheese
- Garlic
- Apples
- Herbal Teas
There are some probiotic strains that are lab grown and can only be taken through supplements. These probiotic strains are selected to go through your stomach acid and can be more effective for the purpose of targeted treatment. For general benefits, you can consume any of the foods listed above.
Precautions and Side Effects
Eating probiotic foods or taking probiotic supplements within recommended range would rarely result in a side effect. In fact, probiotics are prescribed to control the side effects of other drugs, especially for antibiotic-induced diarrhea. Nonetheless, probiotics may still cause Bloating and cramps due to gas.
Consult your doctor before taking probiotics if you have a compromised immune system because of HIV, ongoing cancer treatment, or suffer from recurrent urinary tract infection.
Takeaways
According to one estimate, humans are carrying more microorganisms on their bodies than their own cells. Many of these microorganisms can be beneficial to our health and are called probiotics. Probiotics are present all over our bodies, but most of them are carried in the gut and in organs like the mouth, urinary tract, lungs, and skin. The most common types of probiotic strains are Lactobacillus or Bifidobacterium groups, which are used to prevent several health issues including immunity response, insulin sensitivity, and mental health. Probiotics can regulate the gut microbiome, increase the production of antibodies against viral infections, decrease proinflammatory signaling molecules, increase insulin secretion and sensitivity, and affect mood, psychological health, and brain function.
In conclusion, probiotics play a crucial role in maintaining our health by promoting homeostasis in the body and repopulating the microbiome with good bacteria. These beneficial bacteria, viruses, and fungi aid in digestion, compete against harmful bacteria, produce vitamins, help in the breakdown of certain medications, and strengthen the cell line of the gut to prevent harmful bacteria from entering our bloodstream.
Increasing the amount of fermented food like kimchi, kefir, kombucha, and dairy products in our diet would help us in receiving the benefits of probiotics which promote better health and long life.